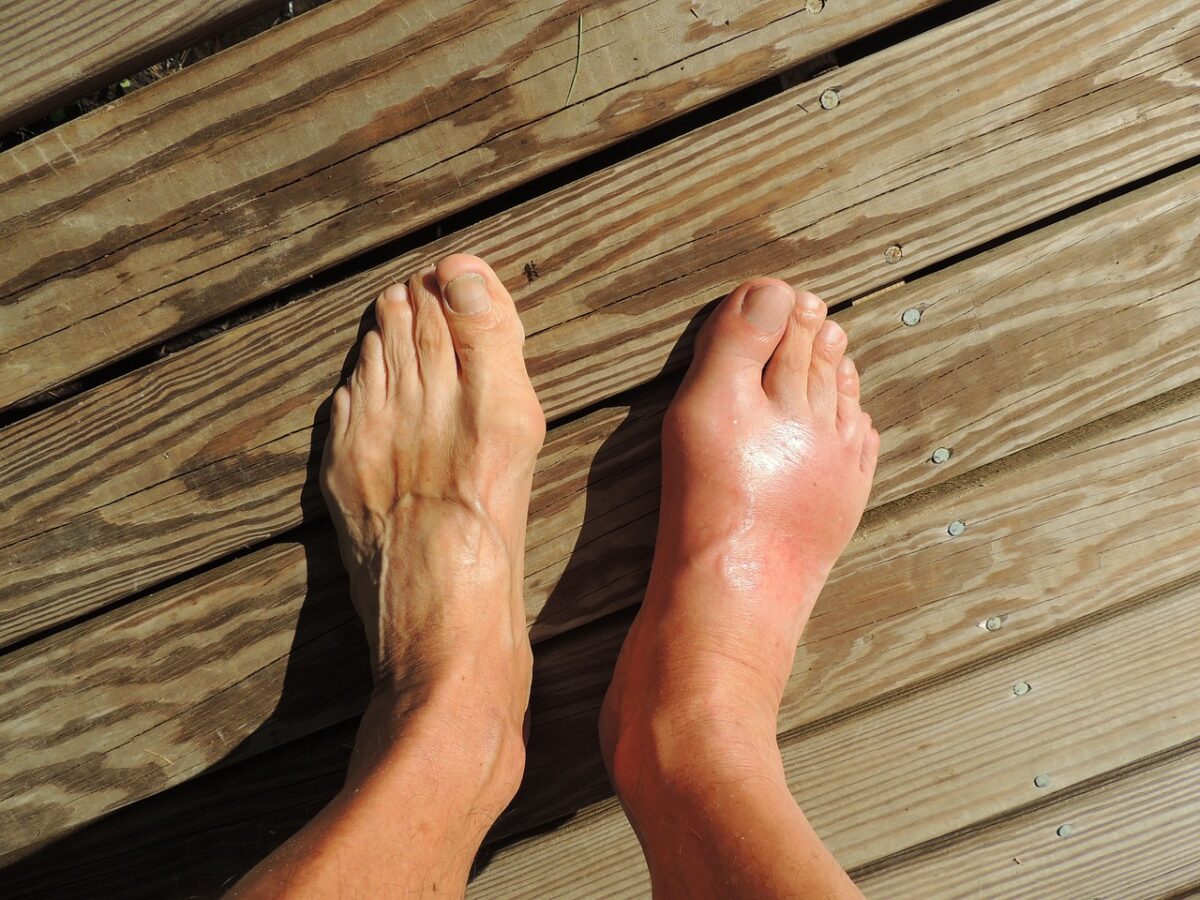
As anyone who’s ever suffered it knows, gout is a horrible business. It’s a metabolic condition which can lead to a build up of uric acid in your system, forming crystals in your joints, and flaring up with nasty pain, swelling and redness in your joints.
As the scientific research into traditional Chinese medicine is becoming more advanced, it has been interesting to see studies done on not just standard acupuncture, but also electroacupuncture and traditional Chinese medicinal bleeding (blood-letting).
Acupuncture for gout
In 2018 a systematic review (a study of all the available studies) concluded that:
Ten RCTs [Randomised Controlled Trials] involving 852 gouty arthritis patients were systematically reviewed. Among them six studies of 512 patients reported a significant decrease in uric acid in the treatment group compared with a control group, while two studies of 120 patients reported no significant decrease in uric acid in the treatment group compared with the control group. The remaining four studies of 380 patients reported a significant decrease in visual analogue scale score in the treatment group … The results of the studies included here suggest that acupuncture is efficacious as complementary therapy for gouty arthritis patients.”
Electroacupuncture for gout
Electroacupuncture is a technique which uses a small machine with wires and clips, to apply a small electric current across some of the acupuncture needles. Generally this gives an odd, tapping, kind of feeling, rather than being painful. In 2024, a research team did a systematic review and meta analysis (where the data from multiple studies is pooled and re-examined) and found that:
“This systematic review examined 15 randomized controlled trials that investigated the use of electroacupuncture as a treatment for AGA [Acute Gouty Arthritis] … The current meta-analysis suggests that electroacupuncture and conventional treatments have comparable efficacy and safety in targeting painful symptoms in patients with AGA … Our study showed that when electroacupuncture and medication were used together, there was a more significant decrease in serum uric acid than alone.”
Traditional Chinese medicinal bleeding (blood-letting) for gout
A 2022 systematic review and meta analysis is not presented in the most accessible language, but it concluded that:
“BLT [Blood-Letting Therapy] is effective in alleviating pain and decreasing CRP level [serum C-reactive protein] in AGA [Acute Gouty Arthritis] patients with a lower risk of evoking adverse reactions.”
CRP is a blood test that is indicative of your body’s level of inflammation.
More research ongoing
All three studies (like other studies into many different kinds of medical intervention) also noted limitations in the evidence base to date, and encouraged further research into these topics.
I was surprised to find all three of these systematic reviews on this topic, it’s fabulous to see the evidence base moving forwards! I look forward to hearing what comes next.
Try Chinese Medicine for your gout symptoms
I offer all three of these treatments, in a fully tailored approach driven by your individual needs and preferences. To see if they may be able to help in your case, just get in touch.
References